We are going to learn how to automate build and deployment of Springboot Microservices Docker Container into Elastic Kubernetes Cluster(EKS) using Helm and Jenkins pipeline.
What is Helm?
Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes. Helm is the K8s equivalent of yum or apt. I
To learn more about Helm, please click here.
Sample springboot App Code:
I have created a sample Springboot App setup in GitHub. Click here to access code base in GitHub.
Jenkins pipeline will:
- Automate maven build(jar) using Jenkins - Automate Docker image creation - Automate Docker image upload into Elastic container registry(ECR) - Automate Springboot docker container deployments into Elastic Kubernetes Cluster using Helm charts
Pre-requisites: 1. E KS cluster needs to be up running. here to learn how to create Amazon EKS cluster.2. Jenkins instance is up and running
3. Install AWS CLI on Jenkins instance 5. Install Kubectl on Jenkins instance 6. Install eksctl on Jenkins instance 8. Make sure to Install Docker, Docker pipeline
10. Dockerfile created along with the application source code for springboot App. 11. Namespace created in EKS cluster
The Code for this video is here:
Create Helm chart using helm command
Go to your root of repo where you have source code for your springboot application. Create helm chart by executing below command:
helm create mychart
Execute the above command to see the files created.
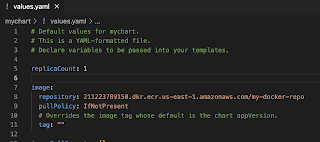
Add Docker image details to download from ECR before deploying to EKS cluster
open mychart/ values.yaml.
Enter service type as LoadBalancer
And also
open mychart/templates/deployment.yaml and change containerPort to 8080
Save the files, commit and push into repo.
Step # 1 - Create Maven3 variable under Global tool configuration in Jenkins
Make sure you create Maven3 variable under Global tool configuration.
Step # 2 - Create a namespace in EKS
kubectl create ns helm-deployment
Step # 3 - Create a pipeline in Jenkins
Create a new pipeline job.
Step # 4 - Copy the pipeline code from below Make sure you change below red marked values as per your settings highlighted in yellow below:
pipeline {
tools {
maven 'Maven3'
}
agent any
environment {
registry = " account_id .dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-docker-repo"
}
stages {
stage('Cloning Git') {
steps {
checkout([$class: 'GitSCM', branches: [[name: '*/master']], doGenerateSubmoduleConfigurations: false, extensions: [], submoduleCfg: [], userRemoteConfigs: [[credentialsId: '', url: ' https://github.com/akannan1087/docker-spring-boot ']]])
}
}
stage ('Build') {
steps {
sh 'mvn clean install'
}
}
// Building Docker images
stage('Building image') {
steps{
script {
dockerImage = docker.build registry
dockerImage.tag("$BUILD_NUMBER")
}
}
}
// Uploading Docker images into AWS ECR
stage('Pushing to ECR') {
steps{
script {
sh 'aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin account_id .dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com'
sh 'docker push account_id .dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-docker-repo:$BUILD_NUMBER'
}
}
}
stage ('Helm Deploy') {
steps {
script {
sh " helm upgrade first --install mychart --namespace helm-deployment --set image.tag=$BUILD_NUMBER"
}
}
}
}
}
Step # 5 - Build the pipeline
Step # 6 - Verify deployments in EKS
Execute the below command to list the helm deployments:
helm ls -n helm-deployment
kubectl get pods -n helm-deployment
kubectl get services -n helm-deployment Steps # 7 - Access Springboot App Deployed in EKS cluster
Once deployment is successful, go to browser and enter above load balancer URL mentioned above
You should see page like below:
Cleanup EKS Cluster using eksctl
To avoid charges from AWS, you should clean up resources.
eksctl delete cluster --name demo-eks --region us-east-1
Watch steps in Youtube channel:
VIDEO
Errors during Deployment:
If you are running into any Deployment errors like below from the pipeline, you can fix it by downgrading helm version.
Root cause and fix:
Downgrading helm version to 3.8.2 would resolve the issue.
curl -L https://git.io/get_helm.sh | bash -s -- --version v3.8.2
Click here for more information













No comments:
Post a Comment